You can learn about low ovarian reserve and why your egg count is important on this blog. You will learn the early warning signs your body gives you, such as periods that don’t come on time, low AMH, or trouble getting pregnant, and what tests can confirm it. Also, it discusses the real reasons for low egg reserves and how fertility doctors identify and treat them. Most importantly, you’ll learn that you can still get pregnant even if you have fewer eggs, with the proper care, support for your lifestyle, and treatment at the right time. This blog is meant to help you understand, feel better, and have hope as you try to get pregnant.
Connect with Fertility World Specialists Today — Get a Free Ovarian Reserve Consultation +91 9311850412 |Email- info@fertilityworld.in
Understanding the Early Signs of Low Ovarian Reserve in Women
Every woman has a certain number of eggs present in their body. It affects each of us in different ways, like a quiet clock.. The number of eggs naturally goes down over time, but for some, it happens faster than imagined. Low ovarian reserve in women means that the ovaries don’t hold as many good eggs as they should for a person of that age.
Your ovarian reserve tells you how many and what kind of eggs are still in your ovaries. The chances of getting pregnant naturally can go down if the amount or quality drops faster than it should, but that doesn’t mean it’s impossible. If you know the signs of low egg reserve, like periods that don’t come on time, fertility drugs that don’t work as well, or lower hormone levels, you can catch problems early.
The first step to taking action based on good information is to learn how to tell if you have low ovarian reserve through simple blood tests and ultrasounds. Many women with low ovarian reserve can still get pregnant and have safe babies if they get medical help at the right time, make changes to their lifestyle, and follow the right fertility plan.
What Is Ovarian Reserve and Why It Matters
The number and quality of eggs that are still in your ovaries are called your ovarian reserve. This is your ability to get pregnant at any age. To put it simply, ovarian reserve is the amount of good eggs that your ovaries can make that can be fertilised. The egg count fertility link is very important because your ovarian reserve has a direct effect on how quickly you can get pregnant on your own or with IVF or other fertility treatments.
The Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) amount is one of the best ways to tell if your ovaries are still working. Because AMH and ovarian reserve are related, checking your AMH can give you a good idea of how many eggs you still have. A higher AMH usually means there are more eggs available, while a lower AMH can mean that the ovarian reserve has been reduced, which can mean that fertility may drop faster than expected.
How Egg Reserve Works
About one to two million eggs are stored in a woman’s ovaries from the time she is born. But over the course of her life, only about 300–500 eggs develop enough to ovulate. The number and quality of eggs a woman lays start to drop more quickly as she ages, especially after age 35.
This normal decline affects fertility, making it harder to get pregnant and slightly lowering the success rates of IVF. If you know how your egg reserve works, you can act quickly, whether you want to get pregnant now or keep your fertility for the future.
Key Hormones That Reflect Egg Reserve
| Hormone/Test | What It Measures | Normal Range | Indicates Low Reserve When |
|---|---|---|---|
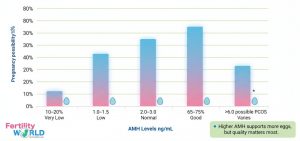
| AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone) | Number of growing follicles | 1.0–4.0 ng/mL | <1.0 ng/mL |
| FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) | Ovarian stimulation capacity | <10 mIU/mL | >10 mIU/mL |
| Estradiol (E2) | Estrogen level on day 3 | 25–75 pg/mL | >80 pg/mL |
| Antral Follicle Count (AFC) | Number of small follicles on scan | 10–20 | <6 follicles |
As the basis of ovarian reserve testing, these hormone tests and ultrasound signs help doctors get a good idea of a woman’s ability to get pregnant.
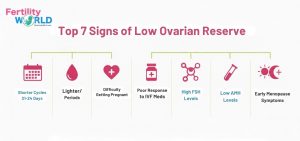
Early Signs of Low Ovarian Reserve
The first signs of low ovarian reserve in women can be mild and are often mistaken for regular changes in hormones. Knowing how to tell if your ovarian reserve is low can help you take charge of your fertility care. This is because egg number and quality decrease over time. A lot of women first notice signs of low AMH or changes in their periods a long time before they have trouble getting pregnant.
Here are the seven most usual signs that something is wrong.
1. Shorter Menstrual Cycles
If your periods are coming every 21–24 days instead of the regular 28–30, this could mean that your follicles are emptying faster. This happens when there are fewer eggs each month, which causes ovulation to happen earlier and chemical imbalances to happen earlier.
2. Lighter or Irregular Periods
One common sign of low ovarian reserve is lighter bleeding or cycles that are missing. As the activity of follicles decreases, estrogen production decreases. This causes endometrial growth to slow down and periods to become shorter and lighter.
3. Difficulty Getting Pregnant
If you can’t get pregnant after 6 to 12 months of trying, it might be because your eggs aren’t good enough or there aren’t enough of them. Many women find out they have a low ovarian reserve when they get pregnancy tests or IVF checks. This is because the ovaries don’t respond well to stimulation.
4. Poor Response to Fertility Medications
Some women make fewer mature follicles during IVF or ovulation induction, even when they take bigger doses of fertility drugs. This is a typical sign of low ovarian reserve, and doctors often call these people “poor responders.”
5. Elevated FSH Levels
On day 3, if the FSH level is higher than 10 mIU/mL, it means that the brain is working harder to get the ovaries to make eggs. One of the main biochemical signs of low ovarian reserve is this, indicating that the ability to produce eggs has begun to decrease.
6. Low AMH Levels
One of the best early signs of low AMH is a level below 1.0 ng/mL. The level of AMH shows how many new follicles there are, which means that there are fewer eggs in the ovaries. AMH measures the number of eggs, but not their quality, which is just as important for a successful birth.
7. Early Signs of Menopause (Perimenopause)
Mood swings, hot flashes, itchy genital areas, or trouble sleeping before age 40 may be signs of ovarian dysfunction or perimenopause, which is another sign of low ovarian reserve.
Medical Causes of Low Ovarian Reserve
To take care of ovulation early, it’s important to know what causes low ovarian reserve. Of course, as women age, their eggs naturally become fewer and of lower quality. But sometimes the ovarian reserve declines more quickly because of something else happening in the body or the way people live. Low AMH is a typical cause of this because it means your ovaries don’t have as many eggs growing. This might happen because of getting older, genetic issues in the family, or some medical treatments.
These are some easy things that can lead to low AMH or low ovarian reserve:
| Category | Examples / Explanation |
|---|---|
| Age-related decline | Natural loss of eggs after 35; egg quality and ovarian response both drop with age. |
| Genetic factors | Conditions like Turner syndrome or fragile X premutation can cause premature ovarian insufficiency. |
| Autoimmune disorders | Diseases affecting the thyroid or adrenal glands can mistakenly attack ovarian tissue, reducing follicle reserve. |
| Endometriosis | Chronic inflammation and scarring around the ovaries can harm follicles and impair egg development. |
| Ovarian surgery | Procedures like cyst removal or laparoscopy may unintentionally damage healthy ovarian tissue. |
| Cancer treatment | Chemotherapy or radiation therapy can destroy ovarian follicles, leading to early menopause or infertility. |
| Lifestyle factors | Habits such as smoking, obesity, stress, or poor nutrition accelerate follicle loss and disrupt hormone balance. |
How Doctors Diagnose Low Ovarian Reserve
Ovarian reserve tests are used to find out if a woman has a low ovarian reserve. Infertility treatments can help determine how many eggs are still in the ovaries and how well they might work with these tests. Blood tests and ultrasound scans that count follicles and measure hormone levels are the most common ways. All of these help your doctor figure out if you might be able to have children before starting treatment.
1. Blood Tests
You need to get blood tests first to find out what your ovarian reserve is. These are the two most important ones:
- AMH test: The Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) test is the most accurate way to find out how many eggs you have. Lower AMH levels mean fewer eggs are growing.
- On the third day of your period, you will get an FSH and Estradiol test. The amounts of Estradiol (E2) and FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) show how hard your body is trying to get the ovaries to work. If FSH or E2 is high, it could indicate a low reserve.
Together, these AMH and FSH tests show how healthy your ovaries are.
2. Ultrasound (Antral Follicle Count)
During this test, an ultrasound is used to count the number of small sacs filled with fluid that are called antral follicles inside your ovaries. These eggs haven’t grown yet, but they might during your next cycle.
- If the scan only shows 5–6 eggs, it could mean that the ovarian reserve is low.
- A healthy AFC scan for fertility generally shows that both ovaries have between 10 and 20 follicles.
This test is easy, doesn’t hurt, and tells you right away how many eggs you have.
3. Ovarian Response in IVF
If you’ve already had IVF, the number of eggs that were collected can help your doctor figure out how your ovaries are responding.
- Even after taking strong medicine, reduced egg production is also a sign of decreased ovarian reserve.
- It means that the cells in your ovaries are still healthy and working.
Doctors use the AMH and FSH test, the ovarian reserve test, and the AFC scan all together to get a full picture of your fertility. This helps them choose the best treatment for you.
Effects of Low Ovarian Reserve on Fertility
It means that a woman doesn’t have many eggs left in her ovaries. Because of this, getting pregnant might be a little harder, but it’s still possible. There are fewer eggs, which means there are fewer chances of ovulation and fewer eggs that can grow into healthy babies. Because of this, low ovarian reserve and infertility go hand in hand.
Women with low AMH may have more trouble getting pregnant on their own. AMH is a hormone that tells women how many eggs they have. Eggs that are still there after age 38 may also have more genetic issues, which can make it harder to get pregnant or even cause loss. Women who don’t have a lot of eggs may need stronger drugs or a different treatment plan during IVF to help their ovaries make more eggs. There are times when the body doesn’t react well, and the doctor may need to end the cycle early.
However, many women with low AMH have become pregnant by getting the right help at the right time. It is important to get tested early, do what your doctor tells you, and keep a hopeful attitude because pregnancy is still possible even if your ovarian reserve is low.
Can You Get Pregnant with Low Ovarian Reserve?
You can still get pregnant even if your ovarian reserve is low. Even though they had low AMH or few eggs, many women have still been able to get pregnant, either on their own or with the help of IVF or other means. Quickly learn about your body and choose the best health plan for you. Your chances of getting pregnant depend on how many good eggs you still have and how your body feels after treatment if you have low AMH.
Natural Conception
If there are still some good eggs in your ovaries, you can still get pregnant on your own. It does happen less often, though, than with women whose egg counts are average. A healthy lifestyle, a well-balanced diet, and fertility products like CoQ10, vitamin D, and folate can improve egg quality and support natural ovulation.
If you want to know the answer to the question “Can I get pregnant with low ovarian reserve?”, it may take more time, work, and preparation.
IVF and Advanced Options
If getting pregnant naturally doesn’t work, fertility procedures are a good option. It only takes a few good eggs for IVF to work and cause a baby.
- A mild stimulus IVF can help your body make eggs that can be used without putting too much stress on your ovaries.
- When the egg quality is low, ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) can improve fertilisation.
- When you don’t have many eggs of your own or they aren’t very good, using donor eggs can help. In most centers, the success rate is over 60%.
With the right care and an upbeat attitude, success is possible even if your egg count is low. Every woman’s journey is different, and science has given us many ways to become mothers.
How to Improve Egg Health and Ovarian Function
Egg count usually goes down as you get older, but there are things you can do to support your ovaries and make your eggs better. You can help your body create a better environment for your eggs by making small changes to what you eat, what you take, and how you live. Following these steps can really help you either build your ovarian reserve or improve your eggs.
1. Nutrient-Rich Diet
For healthy eggs, what you eat is very important. Foods that are high in omega-3, folate, vitamins, and zinc can help protect eggs from damage that comes from stress and getting older.
- Spinach, berries, avocado, eggs, walnuts, and salmon are some of the best things.
Hormone balance and better ovulation are helped by these foods. These are two important parts of ovarian rejuvenation and general fertility health.
2. Supplements
| Supplement | Function | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|
| CoQ10 | Boosts egg cell energy and protects from aging | Women over 30 |
| DHEA | Stimulates ovarian activity and helps egg growth | Women with low AMH or poor IVF response |
| Vitamin D | Regulates reproductive hormones and supports follicle growth | Women with deficiency |
| Myo-Inositol | Improves ovarian sensitivity and egg maturation | Women with PCOS or insulin resistance |
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
Over time, good habits will help your ovaries work better and keep your eggs safe.
- Don’t smoke or drink booze; both lower the number and quality of eggs you lay.
- Stay at a healthy weight (BMI 19–25); being too thin or too heavy can mess up your hormones.
- To naturally balance your hormones, lower your stress level and do yoga, deep breathing, or meditation.
When you do all of these things, your ovaries will feel better and your fertility will improve. This will help your eggs stay stronger and healthier for longer.
Medical Treatments for Low Ovarian Reserve
Don’t give up if you’ve been told you have a low ovarian reserve. There are a number of treatments available today for low ovarian reserve in women that can increase your chances of getting pregnant. These treatments are meant to help your body make better eggs, even if it doesn’t make many. Doctors usually make a plan just for you based on your age, hormone levels, and how IVF has worked for you in the past.
| Treatment | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Tailored IVF Protocols | Uses special IVF protocols for poor responders. Instead of high stimulation, mild or natural IVF cycles focus on fewer but higher-quality eggs. |
| Dual Trigger Injections | Combines two hormones to help eggs fully mature before retrieval, improving fertilization chances. |
| PRP Ovarian Rejuvenation | A new ovarian rejuvenation therapy where platelet-rich plasma is injected into the ovaries to stimulate dormant follicles and improve egg growth. |
| Donor Egg IVF | Recommended when egg count or quality is very low. Using a donor egg can give high success rates, often over 60%. |
Emotional Wellbeing and Counseling Support
When you find out you have a low ovarian reserve, it’s normal to feel scared, sad, or worried. Do not forget that you are not alone and that there are ways to stay strong and upbeat.
It’s easy to understand in this way:
- You can feel sad or angry – You could feel scared, guilty, or even angry. It’s normal to feel this way when you’re having trouble getting pregnant.
- Talk to a person you believe in – Telling your partner, a friend, or a psychologist what’s on your mind can help you feel better and give you support.
- Join a group that can help – It helps to know you’re not alone in this journey when you talk to other women who are going through the same thing.
- Talk therapy can help your heart get better – You will learn how to be stress free, stay cheerful, and think about what you can do next from a fertility counsellor.
- Don’t forget that you have choices -You can have children even if your ovarian reserve is low. There are still many ways we can help you.
- Also, take care of your mind -It’s important to take care of your mind as well as your body. You can clear your mind by doing yoga, meditating, or just taking deep breaths.
- Keep your hopes up -This is not the end of your trip; it’s just the start of a new one full of care, choices, and chances.
Final Thoughts — Fewer Eggs Don’t Mean No Hope
Your path to motherhood may be a little different if you have a low ovarian reserve, but it doesn’t have to end there. Many women who have had trouble getting pregnant because they had low ovarian reserve have still become mothers, some on their own and others with the help of modern fertility treatments.
By following healthy habits and taking the right vitamins, you can improve the health of your eggs, your AMH levels, and your chances of getting pregnant. Remember that success isn’t just about having a lot of eggs. It’s also about time, care, and getting the right kind of help.
Numbers don’t show how fertile a woman is; care, patience, and science that grows with hope do.
Just give us a call when you’re ready to move on. An Ovarian Reserve Consultation at Fertility World can help you feel confident and ready to start the process of becoming a mother.
Remember that success isn’t just about having a lot of eggs
How can I test my ovarian reserve?
Blood tests and ultrasound scans are used by doctors to check ovarian reserve. AMH, FSH, and Antral Follicle Count (AFC) tests help find out how many eggs are present and how the ovaries are responding. These tests are easy and can be done at any pregnancy center.
Can ovarian reserve be improved naturally?
A diet full of nutrients, supplements like CoQ10 and vitamin D, and a stress-free living can all help your ovarian health. You can't make more eggs, but healthy habits can improve the quality of the eggs you do have and your total fertility.
What is considered a dangerously low AMH level?
An AMH level below 1.0 ng/mL is considered low, and below 0.5 ng/mL may indicate very limited egg reserve. However, pregnancy is still possible with the right treatment plan and medical guidance.
How long does it take to get pregnant with low AMH?
It's different for each woman. Some people may be able to get pregnant on their own within a few months, while others may need fertility methods like IVF to get pregnant. If you have low AMH, getting tested and treated early on can help you get pregnant.