Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) research aims to clarify the causes of infertility failure. Fertility World’s aim is to streamline procedures, reduce the risk of failure, improve success rates and decrease cost.
- Get complete advice regarding fertility treatment from our Top Fertility specialists.
- Experienced IVF Doctors: High IVF Success Rate.
- Affordable IVF Treatment: Best IVF Centre in pan India.
- Free first consultation: Book an appointment.
- Call/W: 919311850412 Email: info@fertilityworld.in
IVF is the most efficient form of assisted reproduction technology. It can be performed by using eggs of a couple’s own and the sperm. Or IVF could include eggs, sperm, or embryos of a known or unknown donor. In some instances, the use of a gestational carrier that is, someone with an embryo implanted inside the uterus can be utilized. IVF (IVF) can be described as a complicated set of procedures that aid in fertility or prevent genetic issues and aid in the conception of a baby.
During IVF, the mature eggs are taken (retrieved) from the ovaries and then fertilized by the sperm produced in a laboratory. The fertilized eggs (embryo), as well as eggs (embryos), can be transferred into the uterus. A full cycle IVF is about three months. It is possible to split these steps into multiple parts, and the process maybe longer. The chances of being a healthy mother are increased by IVF depending on a variety of variables, including your age and the reason for infertility. Fertility World’s doctor can assist you to determine how IVF works, the possible risks and the potential risks and infertility is suitable for you.
When should you opt of IVF?
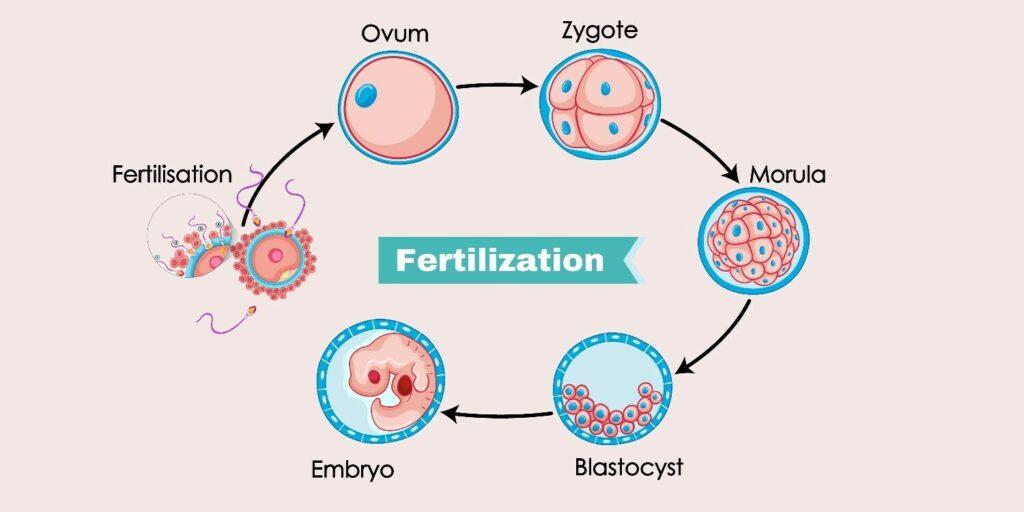
IVF is an effective method of treatment to treat infertility and genetic issues. If you and your partner are suffering from infertility, you may be able to explore alternative treatments that are less invasive prior to attempting IVF or the additional treatments which are even offered simultaneously, this includes fertility drugs that increase the production of eggs, or intrauterine insemination a procedure where the sperm is inserted directly into the uterus at the moment of the ovulation.
Sometimes, IVF is used as a primary treatment for infertility among women who are over 40. IVF It is also possible to do this in the event of specific health issues. For instance, IVF could be a viable option if you or your spouse has:
- Fallopian tube blockage or damage: Fallopian tube damage or blockage can make it difficult for eggs to fertilize or for the embryo to go to the uterus.
- Ovulation problems: If ovulation is not frequent or absent, it means that fewer eggs are fertilized.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to that of the inner lining of the uterus develops and extends beyond the uterus, often impacting the functions of the uterus, ovaries as well as fallopian tube.
- Uterine fibroids: Fibroids are benign cancers of the uterus. They are prevalent among women who are in their 30s and 40s. Fibroids may hinder the fertilization of fertilized eggs.
- Prior tubal sterilization or removal: Tubal Ligation is a form of sterilization where fallopian tubes are cut or blocked in order to stop the possibility of pregnancy. If you want to have a baby after tubal ligation, It could be an alternative for tubal-ligation reversal surgery.
- Affected sperm production, or functioning: Below-average sperm concentration and sperm movement that is weak (poor mobility) or other irregularities in the size and shape of sperm could make it difficult for the sperm of an egg to fertilize. If abnormalities in the semen are discovered it is recommended to visit an expert in infertility to determine whether there are any issues that can be corrected or health issues underlying.
- Unexplained Infertility: Unexplained infertility means that no cause for infertility has been identified despite a thorough examination of common causes.
- A genetic disorder that is genetic: In the event that you or your spouse may be at risk of passing on a genetic condition in your baby, you could be eligible for preimplantation testing which is a procedure that requires IVF. After the eggs have been harvested then fertilized they are tested for specific genetic disorders but there are many genetic issues that can’t be detected. The embryos that do not have any known problems may be transferred into the uterus.
- Preserving fertility for cancer or other medical conditions: If you’re planning to begin chemotherapy or other treatments for cancer, for example, chemotherapy or radiation — which may harm your fertility, IVF is the easiest way to preserve fertility could offer a possibility. Women may be able to harvest eggs from their ovaries and store them in an unfertilized condition to be used later. The eggs could be fertilized and stored as embryos to use later.
Women who do not have a functioning uterus or who are pregnant and pose the risk of serious health problems could opt for IVF having another person use a third person (gestational carriers). In this instance, the woman’s eggs are fertilized by sperm, and the embryos born are then placed into the uterus of the gestational carrier.
How do you Prepare for IVF?
The rate at which a clinic’s success is based on a variety of aspects. This includes the age of patients and medical conditions and the clinic’s patient population as well as various methods of treatment. Request specific information on the expenses for each stage of the process.
Before starting a cycle of IVF using your eggs as well as using sperm from your own eggs you and your spouse will require various tests, such as:
- Testing of the reserve of your ovaries: To determine the amount and the number of eggs your doctor will determine the level of follicle-stimulating follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Estradiol (estrogen) as well as an anti-mullerian hormone in the initial two days of menstrual cycles. The results of tests, which are often utilized in conjunction with an ultrasound scan of your ovaries, can aid in predicting the response of your ovaries to fertility drugs.
- Analysis of Semen: If it is not in your first fertility assessment the doctor will perform an analysis of the semen prior to the beginning of an IVF treatment cycle.
- Screening for infectious diseases: Your partner and you will be screened together for infectious diseases STD, such as HIV.
- The practice (mock) embryo transfer: Your doctor might perform the transfer of a mock embryo to measure the depth inside your uterine cavity, and the procedure that will successfully implant the embryos in the uterus.
- Uterine exam: The doctor will check the inside lining of your uterus before you begin IVF. It could require a sonohysterography where fluid is injected through your cervix into the uterus and then an ultrasound is used to produce images of the uterine cavity. Also, it could involve the hysteroscopy procedure, where a thin, flexible, illuminated telescope (hysteroscope) is introduced through your vagina and the cervix to your uterus.
Before beginning a cycle IVF, consider important questions, including:
- How many embryos are expected to transfer? The number of embryos transferred will typically depend on the age of the woman and the number of eggs that are retrieved. Because implant rates are higher for women who are older and more embryos are transferred — excluding women with donor eggs or genetically-tested embryos.
The majority of doctors adhere to specific guidelines to ensure that there are no higher-order multiple pregnancies, for example, triplets or even more. In certain countries, there are laws that restrict the number of embryos that may be transferred. Be sure that you and your physician are in agreement on how many embryos to be transferred prior to the transfer process begins. - What do you plan to do with the embryos that are not used? Extra embryos can be stored in a freezer to use in the future over many years. Some embryos may not survive the freezing and thawing procedure but the majority of them will.
The frozen embryos could be used to make future cycles of IVF. It is less costly and less invasive. It is also possible that you are in a position to donate frozen embryos to a different couple or to a research center. You could also decide to throw away embryos that are not used. - How do you deal with having multiple children? In the event that more than one embryo gets transferred into your uterus IVF could result in multiple pregnancies, which can pose the risk of health problems for both you and your children. In certain instances, the fetal reduction method can be employed to assist a woman to deliver fewer babies and lower the risk of health. However, pursuing fetal reduction it’s a big choice that has ethical, emotional, and psychological ramifications.
- Have you thought about the possible complications that could arise from the use of donor embryos, eggs, or sperm or even a gestational carrier? A trained counselor who is knowledgeable about donor issues can assist you to be aware of the issues including what rights the donor has under law. You might also require an attorney to file court documents for you to become legal parents of an embryo implanted.
What can you anticipate?
IVF includes several steps -involves the stimulation of ovaries, egg retrieval involves several steps — sperm retrieval and transfer of embryos. A single cycle IVF, It can take anywhere from two to three weeks. It is possible that more than one cycle be required.
Induction of ovulation
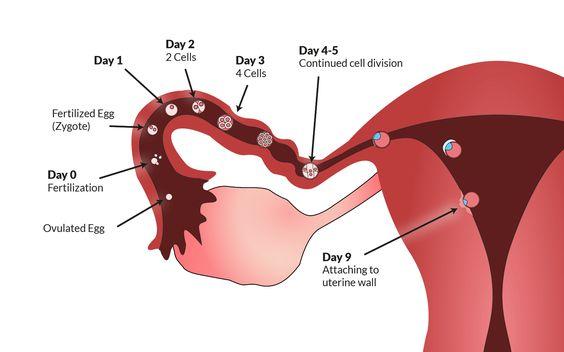
The beginning of an IVF: The cycle starts by using synthetic hormones that stimulate the ovaries and produce several eggs, rather than the one egg that normally develops every month. The need for multiple eggs is as some eggs aren’t fertilized or grow normally the following fertilization.
A variety of different drugs can be utilized, for example:
- Medicines for ovarian stimulation: To stimulate your Ovaries, you could get an injectable drug with a follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) as well as an LH, a luteinizing hormone (LH), or a mix of both. These drugs can cause the development of more than 1 egg to grow at the same time.
- Treatments for maturing oocytes: When the follicles are ready to be used for egg retrieval usually after eight to 14 days you’ll use human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) or any other medication to assist in the maturation of eggs.
- Treatments to avoid premature Ovulation: These medications prevent your body from releasing egg-forming processes too early.
- Medicines to help prepare the liner the Uterus: On the day of egg retrieval, or at the time of embryo transfer, your doctor may recommend that you start taking progesterone supplements in order to make the lining of your uterus open to the process of embryo implantation.
Our Fertility Expert will collaborate together with you to determine the best medication to take and when you should use them. In general, you’ll require between one and two weeks of stimulation to your ovaries before your eggs are ready for collection. To determine if the eggs are ready to be collected You may need:
- Vaginal ultrasound is an examination of your ovaries in order to observe the growth of follicles filled with fluid in ovarian sacs, where eggs develop.
- The blood tests are used for assessing your response to the ovulation stimulants The estrogen levels generally increase when follicles begin to develop while progesterone levels remain lower until after ovulation.
Sometimes IVF Cycles must be stopped prior to egg retrieval due to one of the following reasons:
- Inadequate amount of follicles forming
- Ovulations that are premature
- A large number of follicles are developing which could lead to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
- Other medical concerns
If your cycle has been canceled and your doctor suggests changing the dose of medications to encourage a more effective reaction in the future IVF cycles. You may also be told that you’ll need eggs from a donor.
Egg retrieval

Egg retrieval can be performed at your doctor’s office or in a clinic between 34 and 36 hours following the last injection and prior to the ovulation.
- During egg retrieval, the patient will be sedated and treated with pain medications.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is the most common method of retrieval. A probe of ultrasound is inserted through your vagina to locate the follicles. Then, a needle is placed through an ultrasound guide, which will travel through the vagina and into Foles to extract the eggs.
- If the ovaries of your body aren’t accessible via transvaginal ultrasound An abdominal ultrasound could be utilized to direct the needle.
- The eggs are taken out of the follicles using the needle that is connected to suction equipment. The removal of multiple eggs is completed within 20 minutes.
- After retrieving eggs You may feel discomfort and sensations of fullness or pressure.
- The mature eggs are put in a liquid that is nutritive (culture medium) and then incubated. Eggs that look healthy and mature are mixed with sperm to produce embryos. However, there are a few eggs that can be fertilized.
Sperm extraction
When you’re using the sperm of your loved one for a partner, the semen sample must be delivered to the clinic or office of your doctor on the day of retrieval of eggs. The semen sample is obtained through masturbation. Other methods, for instance, testicular aspiration -the application of needles or a surgical procedure to remove the testicle’s sperm can be required. Donor sperm is also employed. Sperm is separated from semen fluid by the lab.
Fertilization
Fertilization can be accomplished with two different methods:
- Insemination by conventional methods: During conventional insemination, healthy mature eggs and sperm are mixed and then incubated for a night.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI): In ICSI A single healthy sperm is directly injected into each mature egg. A single healthy sperm is injected into each mature. ICSI is usually employed when semen quality or number is an issue, or if attempts to fertilize have failed the preceding IVF cycles failed.
In some situations, your physician may suggest different procedures prior to embryo transfer.
- Aided hatching: Within five to six weeks after fertilization, the embryo “hatches” from its surrounding membrane (zona pellucida) and allows it to be inserted inside the lining of the uterus. In the case of an elderly woman or having suffered from multiple failed IVF In the event of unsuccessful attempts, your physician may consider assisted hatching — the process whereby an opening is created in the zona pellucida prior to transfer in order to assist the embryo to hatch and then implant. Assisted hatching can also be beneficial in the case of embryos or eggs that were frozen prior to transfer because the process may make the zona pellucida harder.
- Genetic testing prior to implantation: Embryos are allowed to grow within the incubator up to a point where a small amount of the embryo can be taken and tested for genetic disorders or for the right number of chromosomes. This is usually within five to six days of growth. Embryos without affected genes or chromosomes could be transferred to the uterus. Although preimplantation genetic testing could decrease the chances that a parent could be able to pass on a genetic condition however it cannot reduce the possibility of developing. A prenatal test is suggested.
Transfer of embryos
Blastocyst
The transfer of eggs is carried out at the doctor’s office or at a clinic. It typically happens between two and five days following the retrieval of eggs.
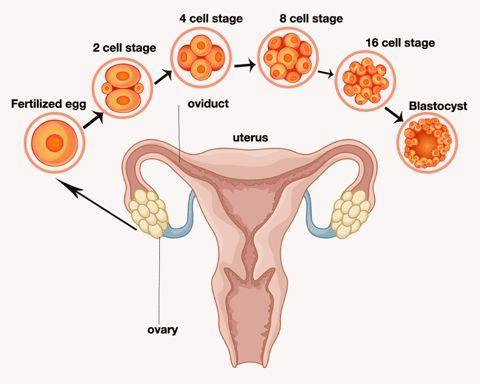
- There is a chance that you will be prescribed a sedative that is mild. The process is generally non-invasive, but you may feel slight cramping.
- The doctor will place a thin, long tubular structure called the catheter inside your vagina, then through the cervix, and then into the uterus.
- A syringe with embryos or other embryos in a small amount of fluid is attached to one tip of the tube.
- With the help of a syringe, the doctor inserts embryos or embryos in the uterus.
If successful, the embryo will develop inside the uterine lining approximately six to ten days after the retrieval of eggs.
Following the procedure
Following the transfer of your embryo is complete, you are able to return to your normal routine. However, your ovaries might be still expanding. Beware of vigorous exercise which may cause discomfort. Common side effects include:
- The passage of a tiny volume of transparent or bloody liquid shortly following the procedure because of the swabbing of the cervix prior to the embryo transfer
- The tenderness of the breasts is due to increased estrogen levels
- A mild bloating
- Mild cramping
- Constipation
If you experience extreme or moderate pain following the embryo transfer, you should consult your physician. They will assess the possibility of complications like inflammation, twisting of an Ovarian (ovarian torsion), and extreme ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Results
In the 12 days to 2 days after retrieving eggs, your doctor will analyze the blood sample to determine whether you’re pregnant.
- If you’re expecting, doctors will recommend the woman to an Obstetrician, or other specialists in pregnancy for care prior to birth.
- In the event that you’re not expecting you’ll stop taking progesterone and most likely have your period in one week. If you aren’t getting your period, or you experience unusual bleeding, consult your physician. If you’re considering the process again with another in vitro fertilization (IVF) Your doctor may recommend steps you can take to increase your chances of having a baby through IVF.
The chance of having healthy babies following the use of IVF is based on a variety of variables, such as:
- Maternal age: The younger you get the more likely you will be able to become pregnant and deliver an unborn baby healthy with your own eggs IVF. Women aged 41 and over are frequently advised to consider the use of donor eggs during IVF to improve the odds of increasing the chances of.
- Status of an embryo: Transfer of embryos that are developed has been associated with higher pregnancy rates when compared to embryos with lower development (day one or two). But there are some embryos that do not remain viable during the process of development. Consult your physician or another health care professional about your particular circumstance.
- Reproductive past: Women who’ve had previous births are more likely to become pregnant IVF as women who’ve never had children. Rates of success have a lower chance of success for females who have previously had a baby IVF multiple times but didn’t get pregnant.
- The reason for infertility: A regular supply of eggs will increase your odds of becoming pregnant IVF. Women with severe endometriosis are more likely to get pregnant IVF more than women with unconfirmed or undiagnosed infertility.
- Lifestyle-related factors: Smokers typically have fewer eggs to be found during IVF and could result in miscarriage more frequently. Smoking reduces the chances of a woman being successful when using IVF by 50percent. Obesity could reduce your odds of becoming pregnant and having a child. Drinking alcohol and recreational drugs, in excess caffeine, and some medications are detrimental.
IVF V/S Long-Term Future
Deciding whether or not to try in vitro fertilization and what steps to take in the event that the first attempt was unsuccessful is a tense choice. The physical, financial, and emotional burden of this procedure can be a challenge.
Talk to us in-depth to find out what your most effective options are and whether it is the best choice for your family and you.


17 thoughts on “What Technology Is Used For IVF”